D.N.A. microneedle was originally developed as a way to deliver active ingredients painlessly into the skin. Dissolvable polymer microneedles are made by mixing active ingredients with dissolvable polymers to create a micron-sized needle shape that naturally dissolves away after skin insertion.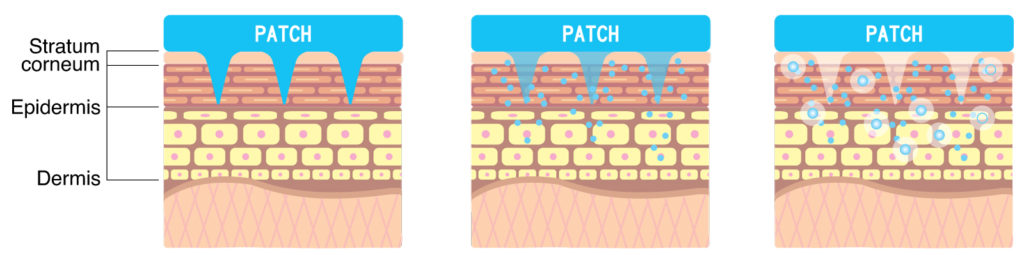
These offer various advantages:
• The microneedle is a painless way of delivering active ingredients compared with the syringe.
This can potentially improve the quality of life for those who would otherwise need frequent injections.
• The dissolvable microneedle is an environmentally friendly solution, leaving no dangerous or wasteful products behind, such as needles or glass, because microneedles dissolve into the skin after insertion.
• Cold-chain supply costs are reduced, because the solid state of the dissolvable microneedle enables greater stability during the distribution of various biopharmaceuticals without the need for refrigeration.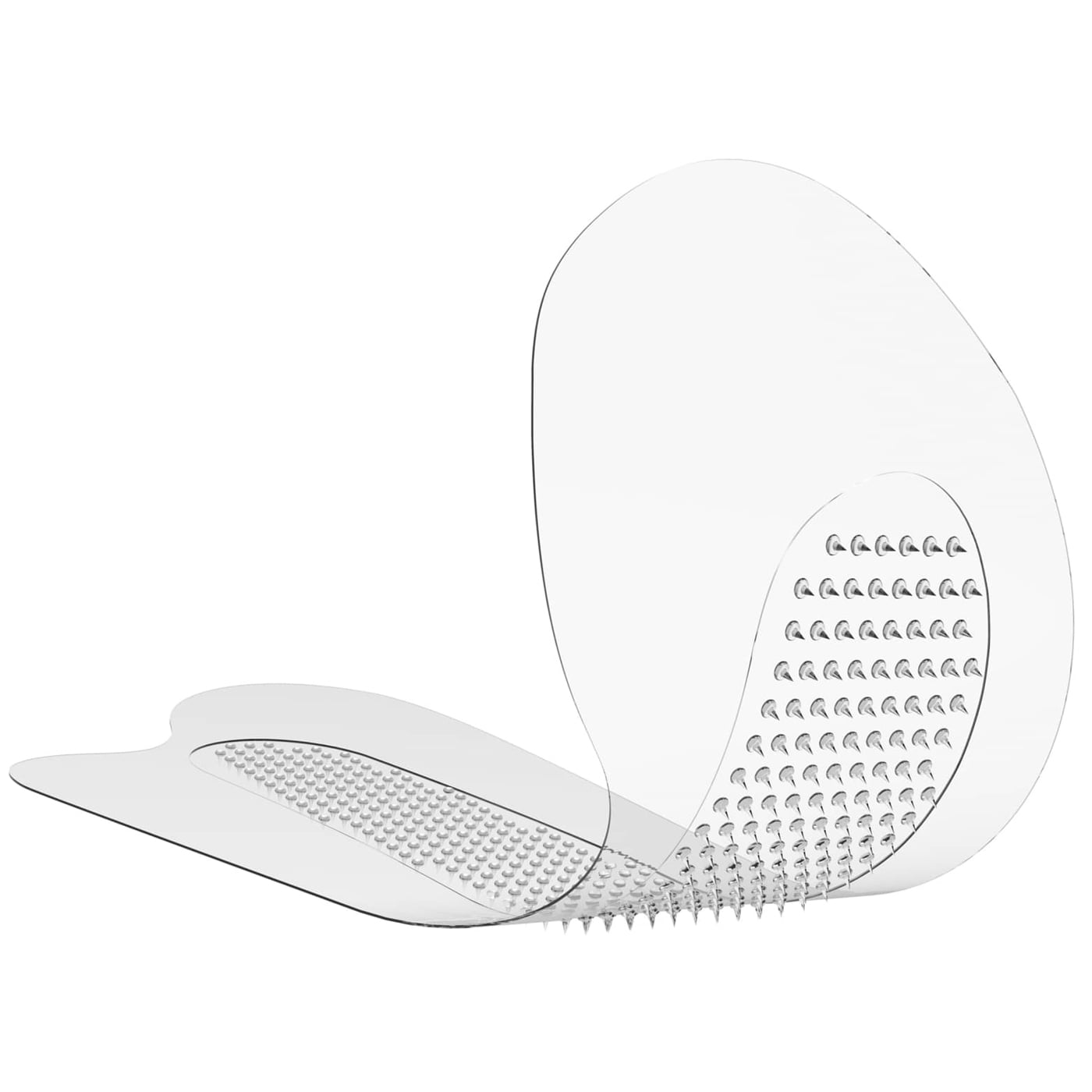
SKINCARE APPLICATIONS
Atrium manufactures skincare microneedle patch products using hyaluronic acid as a matrix material. These skincare products contain various active ingredients with proven effectiveness. In addition, these products are very safe for the skin because they do not contain any preservatives. There were no significant side-effects after using D.N.A. skincare products; this was tested by 25 clinical studies performed according to the good clinical practice guidelines. Also, there were no significant side-effects reported from consumers after using D.N.A. products.
WRINKLE TREATMENT
Facial wrinkles are representative of skin ageing caused by reduction of skin elasticity and degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Tao Radical has commercialized various wrinkle treatment microneedle patch products with a plethora of cosmetic companies. The matrix material of this microneedle is hyaluronic acid, which has been used as moisturizing and filling agent for many cosmetic products. This hyaluronic acid-based microneedle has wrinkle treatment efficacy by itself. Additionally, this product could be combined with a cream or essence type product for better wrinkle treatment efficacy.
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) loaded microneedles showed significant wrinkle treatment efficacy after applying every day for 10 days (Figure 2a). This product also showed significant wrinkle treatment efficacy after applying twice a week for four weeks (Figure 2c).
Figure 2c shows a clinical result which indicates wrinkle improvement efficacy after two hours of application; the peak of observed eye wrinkle was significantly decreased after 2 hours of using the product. These results indicate that this new product has fast-onset efficacy for wrinkle treatment.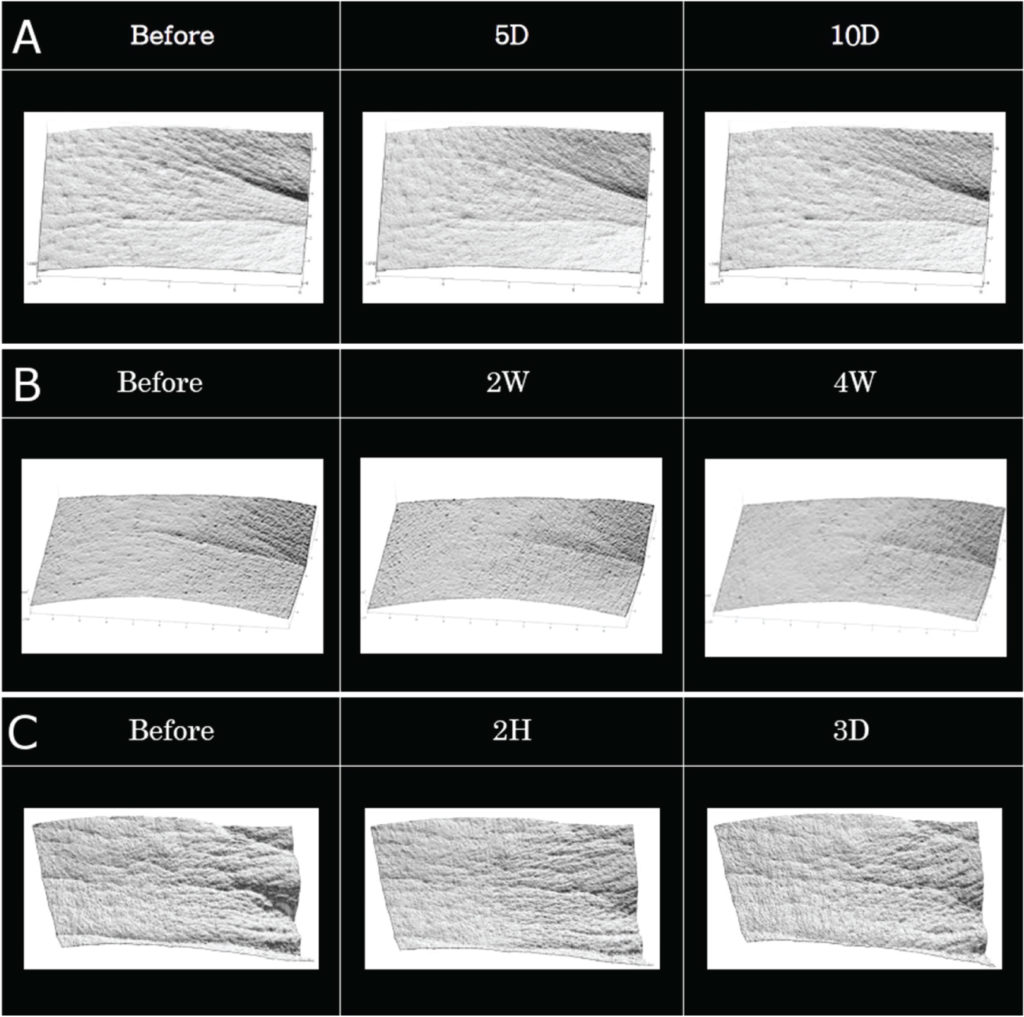 Figure 2: Clinical trial results for wrinkle care efficacy of EGF loaded microneedle patch, with (A) once daily application for 10 days and (B) twice weekly application for 4 weeks. (C) Clinical efficacy of new wrinkle care product after 2 hours of application.
Figure 2: Clinical trial results for wrinkle care efficacy of EGF loaded microneedle patch, with (A) once daily application for 10 days and (B) twice weekly application for 4 weeks. (C) Clinical efficacy of new wrinkle care product after 2 hours of application.
Ingredients
Research
1. McAllister DV et al, “Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: novel fabrication methods and transport studies”. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2003, Vol 100(24), pp 13755-13760.
2. Ito Y et al, “Self-dissolving microneedles for the percutaneous absorption of EPO in mice”. J Drug Target, 2006, Vol 14(5), pp 255-261.
3. Lee JW, Park JH, Prausnitz MR, “Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery”. Biomaterials, 2008, Vol 29(13), pp 2113-2124.
4. Prausnitz MR, Langer R, “Transdermal drug delivery”. Nat Biotechnol, 2008, Vol 26(11), pp 1261-1268.
5. Bal SM et al, “Microneedle-Based Transcutaneous Immunisation in Mice with N-Trimethyl Chitosan Adjuvanted Diphtheria Toxoid Formulations”. Pharm Res, 2010, Vol 27(9), pp 1837-1847.
6. Park JH, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR, “Biodegradable polymer microneedles: fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery”. J Control Rel, 2005, Vol 104(1), pp 51-66.
7. Park JH, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR, “Polymer microneedles for controlled-release drug delivery”. Pharm Res, 2006, Vol 23(5), pp 1008-1019.
8. Gill HS et al, “Effect of microneedle design on pain in human subjects”. Clin J Pain, 2008, Vol 24(7), pp 585-594.
9. Sullivan SP, Murthy N, Prausnitz MR, “Minimally invasive protein delivery with rapidly dissolving polymer microneedles”. Adv Mater, 2008, Vol 20(5), pp 933-938.
10. Sullivan SP et al, “Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination”. Nat Med, 2010, Vol 16(8), pp 915-920.
11. Lee JW et al, “Dissolving microneedle patch for transdermal delivery of human growth hormone”. Small, 2011, Vol 7(4), pp 531-539.
12. Lee K et al, “Drawing lithography: three-dimensional fabrication of an ultra-high-aspect-ratio microneedle”. Adv Mater, 2010, Vol 22(4), pp 483-486.
13. Kim JD et al, “Droplet-born air blowing: Novel dissolving microneedle fabrication”. J Control Rel, 2013, Vol 170(3), pp 430-436.
14. Yang H et al, “Centrifugal Lithography: Self-Shaping of Polymer Microstructures Encapsulating Biopharmaceutics by Centrifuging Polymer Drops”. Adv Healthcare Mater, 2017, Vol 6(19).
15. Ito Y et al, “Feasibility of microneedles for percutaneous absorption of insulin”. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2006, Vol 29(1), pp 82-88.
16. Indermun S et al, “Current advances in the fabrication of microneedles for transdermal delivery”. J Control Rel, 2014, Vol 185, pp 130-138.
17. Schoellhammer CM, Blankschtein D, Langer R, “Skin permeabilization for transdermal drug delivery recent advances and future prospects”. Exp Opin Drug Deliv., 2014, Vol 11(3), pp 393-407.
18. Nguyen TT, Park JH, “Human studies with microneedles for evaluation of their efficacy and safety”. Exp Opin Drug Deliv, 2017, Vol 30, pp 1-11.
19. Hong JY et al, “Efficacy and safety of a novel, soluble microneedle patch for the improvement of facial wrinkle”. J Cosmet Dermatol, 2017, Oct 7.
20. Kim S et al, “Enhanced Transdermal Delivery by Combined Application of Dissolving Microneedle Patch on Serum-Treated Skin”. Mol Pharm 2017, Vol 14(6), pp 2024-2031.
21. Park J et al, “Efficacy of Biodegradable Microneedle Patches on Periorbital Wrinkles”. Korean J Dermatol, 2014, Vol 52(9), pp 597-607.
22. Goldman MJ, Anderson GM, Stolzenberg ED, “Human betadefensin- 1 is a salt-sensitive antibiotic in lung that is inactivated in cystic fibrosis”. Cell, 1997, Vol 88, pp 553-560.
23. Sieprawska-Lupa M et al, “Degradation of human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by Staphylococcus aureus-derived proteinases”. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2004, Vol 48(12), pp 4673-4679.
24. Cabanes J, Chazarra S, Garcia- Carmona F, “Kojic acid, a cosmetic skin whitening agent, is a slowbinding inhibitor of catecholase activity of tyrosinase”. J Pharm Pharmacol, 1994, Vol 46(12), pp 982-985.
25. Chang TS, “An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors”. Int J Mol Sci, 2009, Vol 10(6), pp 2440-2475.
26. Lee MR, Shumack S, “Prurigo nodularis: a review”. Australas J Dermatol, 2005, Vol 46(4), pp 211-218; pp 219-220.
27. Parisi R et al, “Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence”. J Invest Dermatol, 2013, Vol 133(2), pp 377-385.
28. Lee JH et al, “A hyaluronic acid-based microneedle patch to treat psoriatic plaques: A pilot open trial”. Br J Dermatol, 2018, Vol 178, pp 24-25.
29. Zimmerman S et al, “A microneedlebased glucose monitor: fabricated on a wafer-level using in-device enzyme immobilization”. TRANSDUCERS 2003 – The 12th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, 2003, Vol 1, pp 99-102.
30. Mukerjee E et al, “Microneedle array for transdermal biological fluid extraction and in situ analysis”. Sens Actuators, A, 2004, Vol 114, pp 267-275.
31. Wang PM, Cornwell M, Prausnitz MR, “Minimally invasive extraction of dermal interstitial fluid for glucose monitoring using microneedles”. Diabetes Technol Ther, 2005, Vol 7(1), pp 131-141.
32. Li CG et al, “One-touch-activated blood multidiagnostic system using a minimally invasive hollow microneedle integrated with a paperbased sensor”. Lab Chip, 2015, Vol 15(16), pp 3286-3292.
33. Donnelly RF et al, “Hydrogelforming microneedles increase in volume during swelling in skin, but skin barrier function recovery is unaffected”. J Pharm Sci, 2014, Vol 103, pp 1478-1486.
34. Romanyuk AV et al, “Collection of analytes from microneedle patches”. Anal Chem, 2014, Vol 86(21), pp 10520-10523.
35. Steele LS, Glazier RH, “Is donepezil effective for treating Alzheimer’s disease?”. Can Fam Physician, Vol 45, pp 917-919.
36. Affoo RH et al, “Swallowing dysfunction and autonomic nervous system dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: a scoping review of the evidence”. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2013, Vol 61(12), pp 2203-2213.
37. Kim JH et al, “Successful transdermal allergen delivery and allergen-specific immunotherapy using biodegradable microneedle patches”. Biomat, 2018, Vol 150, pp 38-48.







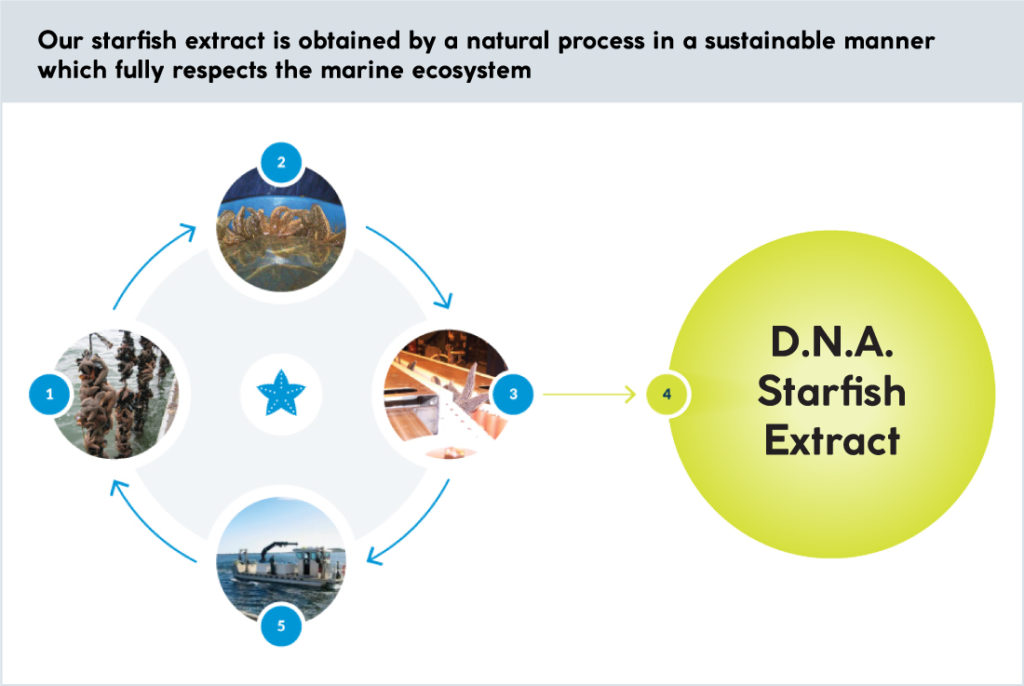
 The video below shows the first 24h of the recolonization process by normal human keratinocytes in culture, comparing the control cells (top) to cells treated with starfish coelomic fluid from D.N.A.’s Asteria vulgaris (bottom).
The video below shows the first 24h of the recolonization process by normal human keratinocytes in culture, comparing the control cells (top) to cells treated with starfish coelomic fluid from D.N.A.’s Asteria vulgaris (bottom).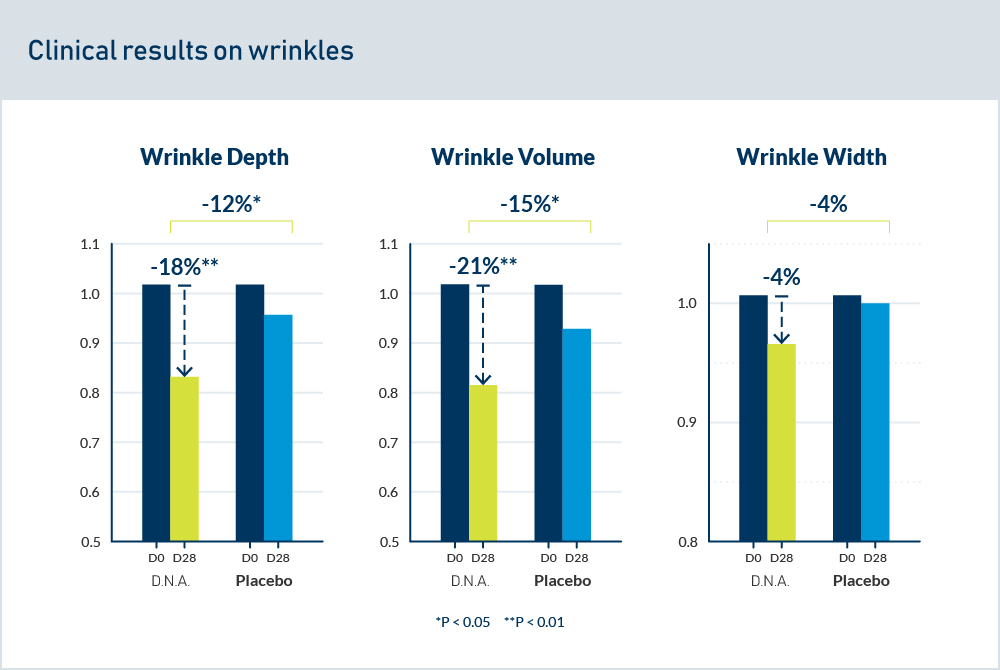
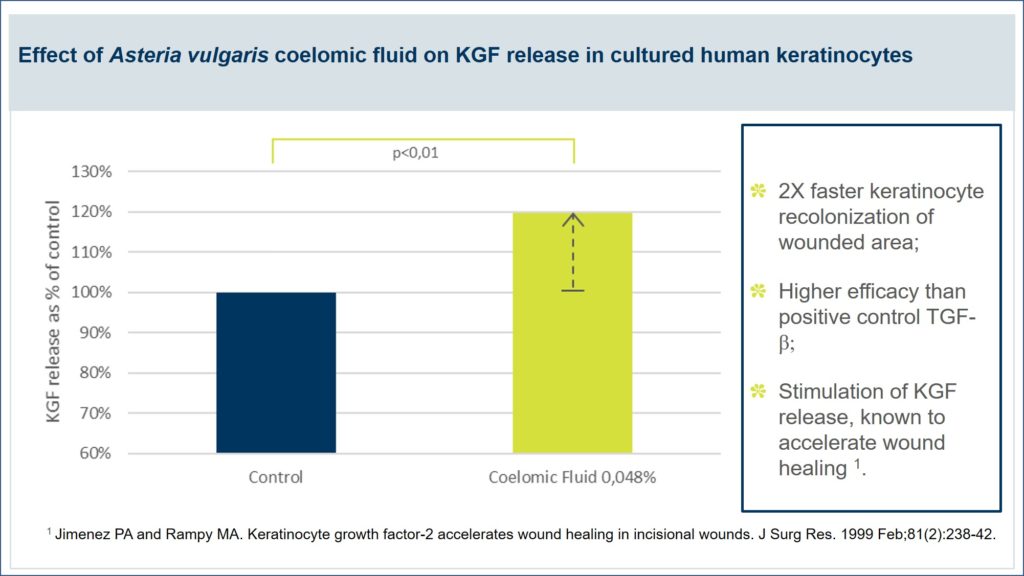 Pictures of the wounded area were taken at baseline (A), and after 24h of recolonization under the control (B), TGF-β (C) or coelomic fluid (D) treatments, showing a clear, positive regenerative impact of coelomic fluid on wound healing process.
Pictures of the wounded area were taken at baseline (A), and after 24h of recolonization under the control (B), TGF-β (C) or coelomic fluid (D) treatments, showing a clear, positive regenerative impact of coelomic fluid on wound healing process.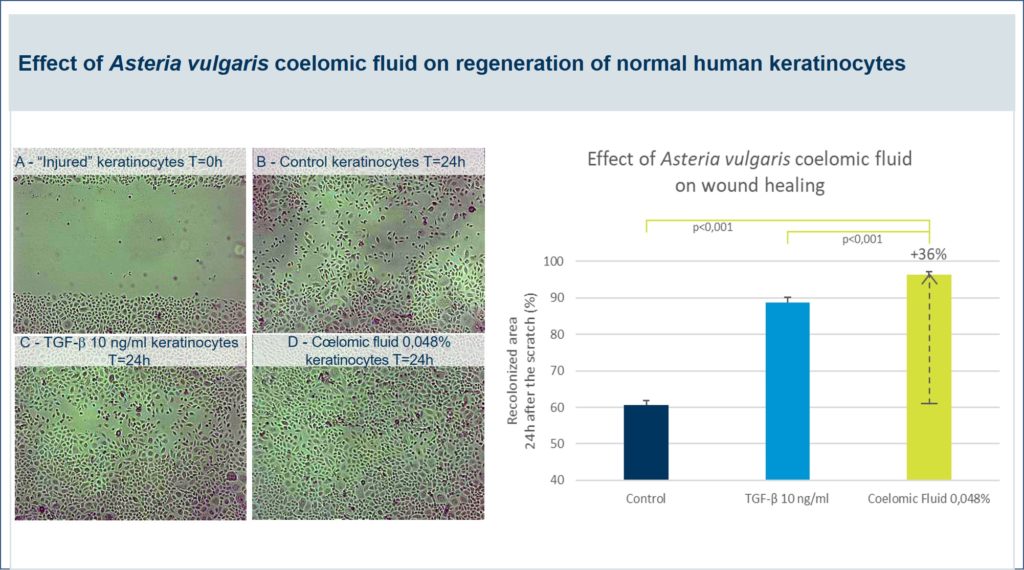
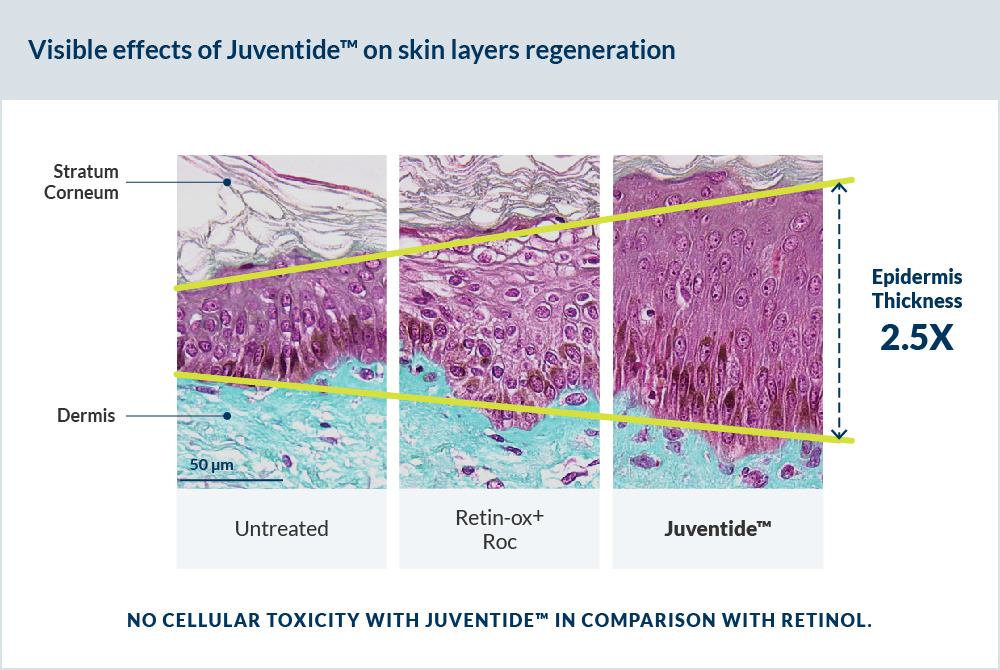
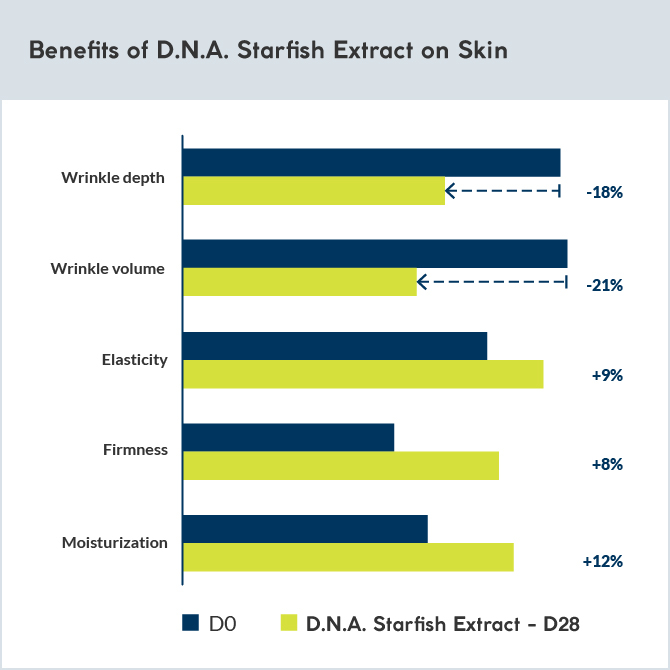
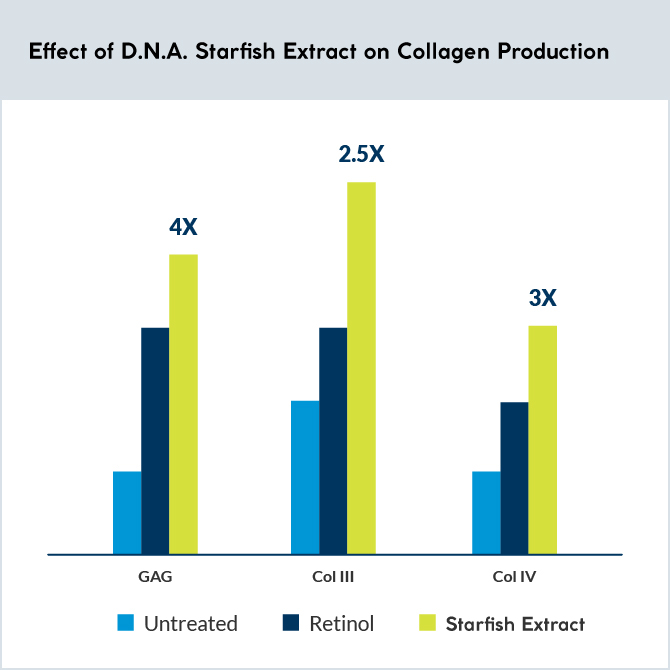 Analysis of type III and IV collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis after 6 days of topical application of 1.6% D.N.A. Starfish Extract (or retinol cream) was performed on skin explants from a 60-year-old female donor.
Analysis of type III and IV collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis after 6 days of topical application of 1.6% D.N.A. Starfish Extract (or retinol cream) was performed on skin explants from a 60-year-old female donor.